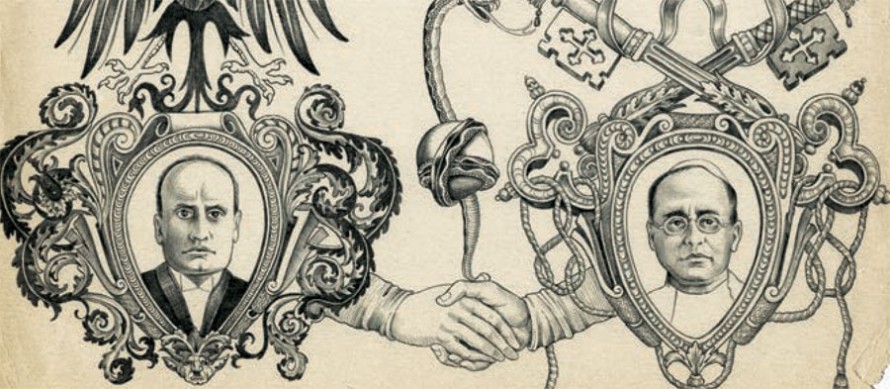
David Kertzer, The Pope and Mussolini: The Secret History of Pius XI and the Rise of Fascism in Europe, Random House, 2014
As David Kertzer demonstrates repeatedly in this nuanced book, to be critical of fascism in Italy in the 30s was not necessarily to be liberal or a lover of democracy. And to be antisemitic was not to be unchristian. The Pope told Mussolini that the church had long seen the need to “rein in the children of Israel” and to take “protective measures against their evil-doing”. The Vatican and the fascist regime had many differences, but this they had in common.
Kertzer announces that the Catholic church is generally portrayed as the courageous opponent of fascism, but this is an exaggeration. There is a counter-tradition, John Cornwell’s fine book, Hitler’s Pope, on Pius XII (who succeeded Pius XI in 1939) exposed the Vatican’s culpable passivity in the face of the wartime persecution of Italian Jews. But Kertzer describes something more fundamental than a church leader’s strategic decision to protect his own flock rather than to speak up in defence of others. His argument, presented not as polemic but as gripping storytelling, is that much of fascist ideology was inspired by Catholic tradition – the authoritarianism, the intolerance of opposition and the profound suspicion of the Jews.
Pius XI – formerly Achille Ratti, librarian, mountain-climber and admirer of Mark Twain – was elected Pope in February 1922, eight months before Mussolini bullied his way to the Italian premiership. For 17 years the two men held sway over their separate spheres in Rome. In all that time they met only once, but they communicated ceaselessly by means of ambassadors and nuncios, through the press (each had his tame organ) and via less publicly accountable go-betweens. From the copious records of their exchanges Kertzer has uncovered a fascinating tale of two irascible – and often irrational – potentates, and gives us an account of some murky intellectual finagling, and an often startling investigation of the exercise of power.
The accession of Mussolini, known in his youth as mangiaprete – priest-eater – didn’t bode well for the papacy. The fascist squads had been beating up clerics and terrorising Catholic youth clubs. But Mussolini saw that he could use the church to legitimise his power, so he set about wooing the clergy. He had his wife and children baptised. He gave money for the restoration of churches. After two generations of secularism, there were once again to be crucifixes in Italy’s courts and classrooms. Warily, slowly, the Pope became persuaded that with Mussolini’s help Italy might become, once more, a “confessional state”.
Only gradually did it become clear how much the church might lose in the process. Pius fretted over inadequately dressed women – backless ballgowns and the skimpy outfits of female gymnasts were particularly worrisome. Mussolini played along, solemnly declaring that, in future, girls’ gym lessons would be designed only to make them fit mothers of fascist sons. He was accommodating in aiding the Pope’s war on heresy – banning Protestant books and journals on demand. But Mussolini was creating a heresy of his own. Schoolchildren were required to pray to him: “I humbly offer my life to you, o Duce.” In January 1938, he summoned more than 2,000 priests, including 60 bishops, to participate in a celebration of his agricultural policy. Neither the Pope nor his secretary of state were happy, but they feared offending the dictator. And so the priests marched in procession through Rome. They laid wreaths, not at a Christian shrine, but on a monument to fascist heroes. They saluted Mussolini as he stood on his balcony and attended a ceremony where they were required to cheer his entrance, to pray for blessings upon him and roar out “O Duce! Duce! Duce!” That the fascists (beginning with their precursor, Gabriele d’Annunzio) had appropriated ecclesiastical rituals and liturgies could perhaps be taken as a compliment to the church, but to recruit its priests for the worship of a secular ruler was to humiliate God’s vicar on earth. Mussolini was cock-a-hoop. It was easy to manipulate the church, he told his new allies in Nazi Germany. With a few tax concessions, and free railway tickets for the clergy, he boasted, he had got the Vatican so snugly in his pocket it had even declared his genocidal invasion of Abyssinia “a holy war”.
When it comes to the “Jewish question”, Kertzer demonstrates that the Pope’s failure to protest effectively against the fascist racial laws arose not simply from weakness, but because antisemitism pervaded his church. Mussolini scored a painful hit when he assured Pius that he would do nothing to Italy’s Jews that had not already been done under papal rule. Roberto Farinacci, most brutal of the fascist leaders, came close to the truth when he announced: “It is impossible for the Catholic fascist to renounce that antisemitic conscience which the church had formed through the millennia.” And Catholic antisemitism was thriving. Among Pius’s most valued advisers were several who – as Kertzer amply demonstrates – saw themselves as battling against a diabolical alliance of communists, Protestants, freemasons and Jews.
Avoiding overt partisanship, Kertzer coolly lays out the evidence; he describes his large and various cast of characters, and follows their machinations. We meet the genial Cardinal Gasparri who, narrowly missing the papacy himself, became Pius’s secretary of state, handling the negotiations that led in 1929 to the Lateran Accords between the Vatican and the regime. Gasparri, a peasant’s son who had risen far, considered Mussolini absurdly ignorant and uncouth; Mussolini thought him “very shrewd”. We meet the Jesuit father, Tacchi Venturi, Pius’s unofficial emissary, a firm believer in conspiracy theories, who claimed to have been nearly killed by an antifascist hitman (the story doesn’t stand up). We meet Monsignor Caccia, Pius’s master of ceremonies, who was known to the police and to Mussolini’s spies for luring boys to his rooms in the Vatican for sex, rewarding them with contraband cigarettes. And we meet the motley crew familiar from histories of fascism: the doltish Starace, Mussolini’s “bulldog”; Ciano, plump and boyish and, in the opinion of the American ambassador, devoid of “standards morally or politically”; and Clara Petacci, the girl with whom Mussolini spent hours of every day on the beach. Some of this is familiar territory, but what is new, and riveting, is how fascists and churchmen alike were forced into intellectual contortions as they struggled to justify the new laws. “Racism” was good. “Exaggerated racism” was bad. “Antisemitism” was good, as long as it was Italian. “German antisemitism” was another thing entirely.
Eventually Pius XI drew back from this casuistry. Kertzer describes the old pope on his deathbed, praying for just a few more days so that he could deliver a speech with the message that “all the nations, all the races” (Jews included) could be united by faith. He dies. Cardinal Pacelli – suave, emollient and devious, where Pius XI was a table-thumper who had no qualms about blurting out uncomfortable truths – clears his desk, suppresses his notes and persuades the Vatican’s printer, who has the speech’s text ready for distribution, to destroy it so that “not a comma” remains. Eighteen days later Pacelli becomes Pope Pius XII. It is a striking ending for a book whose narrative strength is as impressive as its moral subtlety.
• Lucy Hughes-Hallett’s The Pike: Gabriele d’Annunzio has won the Samuel Johnson prize for non-fiction, the Costa biography award and the Duff Cooper prize.