Rita Levi Montalcini, In Praise of Imperfection: My Life and Work, Sloan Catering Foundation Science Series, 1988
Rita Levi Montalcini
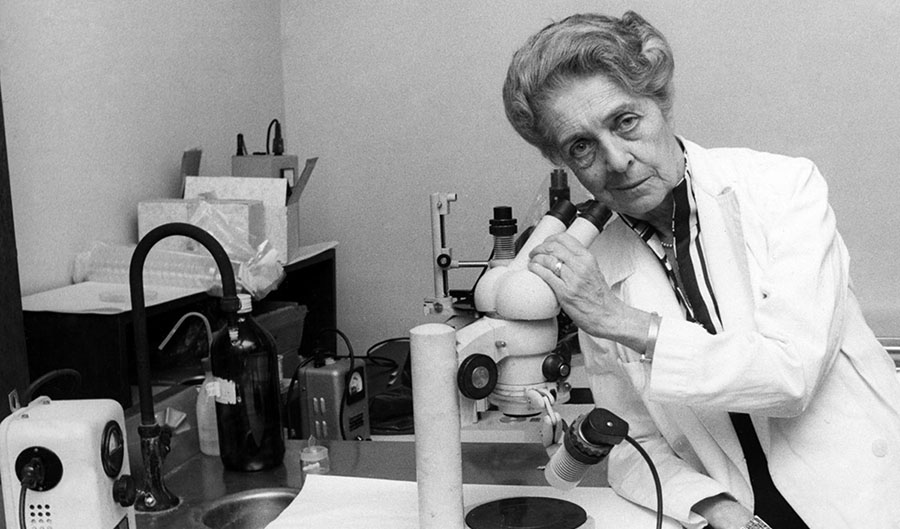
Rita Levi-Montalcini, the longest living Nobel Prize winner, died on December 30, 2012 at the age of 103. She established her fame by discovering the first nerve growth factor, NGF, in the 1950s. Her finding led to the identification of many growth factors, which have greatly influenced developmental biology, neuroscience, immunology and cancer. NGF and related neurotrophins are associated with learning and memory, pain, neurodegeneration (Alzheimer’s and Huntington’s diseases) and psychiatric disorders. Rita Levi-Montalcini represented a breed of scientist rarely seen today. Born into a traditional Italian Jewish family, she endured obstacles due to gender, religion and war. As a woman, her family reluctantly allowed her to pursue her studies and career. After medical school at the University of Turin, she became interested in neurology. However, with the promulgation of the fascist racial laws of 1938, Levi-Montalcini was not allowed to work. During the period of 1940-1943, she carried out her research on early chick embryonic development in a makeshift laboratory in her bedroom. She was eventually forced into hiding by the anti-Jewish persecution. From these early efforts, Levi-Montalcini used chick embryos to study the effects of target tissue upon nerve growth, giving rise to methods that made the isolation of NGF possible. Rita Levi-Montalcini has been an inspiration for many generations of scientists, due to her exemplary life, as a neuroscientist, leader, politician, prolific writer and her dedication to education. Rita was a staunch supporter of women in science. She promoted the careers of young women and established a foundation to assist African women with scholarships to further their education.
Rita Levi Montalcini, In Praise of Imperfection: My Life and Work, Sloan Catering Foundation Science Series, 1988
“This memoir, by one of the world’s most prominent scientific investigators of the nervous system, is an arresting story of someone who insisted on being herself rather than someone else’s idea of herself. The sciences of the brain and nervous system, always daunting, are in the middle of a new revival, fueled by the enormous power of recombinant DNA technology. Rita Levi-Montalcini’s discovery of a protein called ”nerve growth factor,” which fosters the growth of nerve fibers and also plays a role in the brain and the immune system, is one of the most important steps taken so far toward understanding how the fantastically complex system of nerves is laid down and linked to the tissues in a developing embryo. Her account of the adventures leading to this discovery, for which she shared a Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine in 1986, has a special contemporary interest.” Victor K. Mcelheny, The New York Times